Archive for 2006
Rain Network
 In Brazil, the necessity has become the mother of invention. The hinterlands of South America's largest country are virtually inaccessible by roads, and copying and transporting hundreds of reels of film is expensive. Founded in 2002, Rain Network is a brazilian company that has created a solution for independent cinema market by interconnecting theaters in a digital network, with built-in antipiracy measures, and Brazil is poised to take the boldest steps yet into all-digital cinema, with 100 theaters - the largest digital network in the world.
In Brazil, the necessity has become the mother of invention. The hinterlands of South America's largest country are virtually inaccessible by roads, and copying and transporting hundreds of reels of film is expensive. Founded in 2002, Rain Network is a brazilian company that has created a solution for independent cinema market by interconnecting theaters in a digital network, with built-in antipiracy measures, and Brazil is poised to take the boldest steps yet into all-digital cinema, with 100 theaters - the largest digital network in the world. The creative spark that was harnessed for more practical ends by Rain when they sought to develop a new digital exhibition and distribution platform. Using Windows Media 9 software, engineers came up with MPEG-4, video compression software that is cheaper and faster than the current system. The MPEG-4 software can squeeze a feature film onto a file of just five gigabytes, 15 times smaller than the MPEG-2 technology presently used.
The films are then beamed by satellite from Rain's central computer in Sao Paulo to picture houses across the country. Depending on bandwidth, it can take as little as 20 minutes to send a 90-minute film to a theater.
By eliminating celluloid and transport costs, distributors could quickly and cheaply beam blockbusters to distant towns the same day as they première in London, Los Angeles, or Sao Paulo. They can offer a wider range of films and even live broadcasts.
With offices in Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, New York and London, Rain Network currently transmits, by satellite, films in digital format to more than 106 screens in Brazil, 14 screens in US and one screen in UK.
Rain Network
Av. Eng. Luiz Carlos Berrini 500 - cj 21
CEP 04571-000 - Sao Paulo - SP
Phone: (+5521) 2164-9797
Site: http://www.rain.com.br
MVC Wall System
 Wall System is a technology for civil construction. Because of its distinguished characteristics of manufacturing and flexibility it can be used for low-cost constructions, such as schools, health centers, hostels and beach houses, among many other applications. The exclusive Wall System boards are made of a sandwich-like structure with fiberglass-reinforced plastic panels and a special core to meet both Brazilian and International standards.
Wall System is a technology for civil construction. Because of its distinguished characteristics of manufacturing and flexibility it can be used for low-cost constructions, such as schools, health centers, hostels and beach houses, among many other applications. The exclusive Wall System boards are made of a sandwich-like structure with fiberglass-reinforced plastic panels and a special core to meet both Brazilian and International standards.As one of its great differentials, this system allows large-scale construction in a very short period of time. It also doesn't need painting and can be manufactured in different colors. According to the type of project, the customer can choose from wood, iron or aluminum doors and windows. Approved in all the resistance tests carried out by IPT - Instituto de Pesquisas Tecnológicas (Institute for Technological Research) at USP (SP), the Wall System technology also allows fine thermal and acoustical insulation.
Developed by MVC, a company belonging to Marcopolo S.A., that was founded in 1989, in São José dos Pinhais, PR, Brazil.
By improving and applying certain processes such as Vacuum Forming, Light RTM (Resin Transfer Molding), Continuous Lamination and Polyurethane Injection (PU), MVC started its activities operating in the Automotive Industry and gradually broadened its operations, introducing its own plastic products to the Light Industry and Infra-structure markets.
MVC has presently four manufacturing plants: three in Brazil (São José dos Pinhais - PR, Catalão - GO and Caxias do Sul - RS) and one abroad (Poloplast in Monterey, Mexico). MVC is always surprising with constant innovations and the search for improvement on plastic technology is always converted into distinguished products for the domestic and foreign markets.
MVC Componentes Plásticos Ltda.
Rua Maria Isabel Zagonel, 205
São José dos Pinhais, PR, Brazil
CEP: 83045-430
Phone: +55. 41. 2141.3200
Site: http://www.marcopolo.com.br/
Tritec Motors
 Tritec Motors Ltda. was born from a joint venture established in 1996 between BMW and Chrysler with the objective to manufacture 1.4 and 1.6 liter gasoline engines in Brazil. Today, Tritec is the result of an investment of this US$ 500 million in equal shares.
Tritec Motors Ltda. was born from a joint venture established in 1996 between BMW and Chrysler with the objective to manufacture 1.4 and 1.6 liter gasoline engines in Brazil. Today, Tritec is the result of an investment of this US$ 500 million in equal shares.The plant was built in the town of Campo Largo in the Curitiba metropolitan area, in the state of Paraná, on a lot of 1.27 million square meters. Construction began in 1998 and by January 1999, Tritec's 40,000 square meter facility had already been constructed.
The first motor was assembled in September of that same year. Tritec enters 2003 with an output capacity of 400 thousand motors/year.
Built according to strict quality and technology standards, the gasoline powered, 4-cylinder, 16 valve 1.6/1.4 liter engines are destined for export, equipping all BMW Mini models world wide; the DaimlerChrysler PT Cruiser in South Africa, Europe, and other foreign markets; and an additional export variant of the DaimlerChrysler Neon.
Tritec's forward vision, desire for success, investment in technology, investment in human resources, modern management techniques, and high level of automation, place Tritec among the world's best engine manufacturers which is clearly reflected in the final quality of its products.
Tritec Motors S.A.
Rua Ema Tanner de Andrade, 1892.
Campo Largo-PR
Telephone: 55 41 391-4500
Fax: 55 41 391-4551
Site: http://www.tritecmotors.com.br
WEG
 Werner Ricardo Voigt (W), Eggon João da Silva (E) and Geraldo Werninghaus (G) founded "Eletromotores Jaraguá" in 16th of September 1961, three years later, the company created by an electrician, an administrator and a mechanic changed its name to "Eletromotores WEG SA".
Werner Ricardo Voigt (W), Eggon João da Silva (E) and Geraldo Werninghaus (G) founded "Eletromotores Jaraguá" in 16th of September 1961, three years later, the company created by an electrician, an administrator and a mechanic changed its name to "Eletromotores WEG SA".Dedicated initially to the production of electric motors, the Company expanded its activities in the 1980s through the production of generators, electrical components, industrial automation products, power and distribution transformers, liquid and powder paints, and electro-insulating varnishes. Its product lines include control and protection, electric motors, generation and distribution of energy, industrial paints and varnishes, industrial process automation and speed variation.
Counting on more than 14 thousand employees all over the world, WEG reached an annual turnover of R$ 2.978 billion in 2005, a growth of 14% in relation to 2004, R$ 2,608 billion. Exports were responsible for almost 40% of the company's turnover. Production is concentrated in seven manufacturing plants in Brazil (in th cities of São Paulo, São Bernardo do Campo, Guarulhos, Manaus, Guaramirim, Blumenau and two plants in Jaraguá do Sul, two in Argentina, one in Mexico, one in Portugal and one in China. WEG also exports to over 100 countries and counts on branches and technical assistance in all five continents.
A good part of these great results influence life in the city of Jaraguá do Sul directly. One of the most visible forms of this is the distribution of profits to the employees. Besides the injection of capital that the profit distribution provokes in all the sectors of the economy, WEG also participates directly in the increase in quality of life of the city.
WEG S.A.
Av Prefeito Waldemar Grubba, 3330
Jaragua Do Sul, 89256-900
BRA +55-0047-3724000 (Phone)
Site: http://www.weg.com.br
Cryopraxis Cryobiology
 Cryopraxis Cryobiology is a company dedicated to the collection, transportation, processing, freezing, long-term storage and biologic analyses of stem cells in the blood of the umbilical cord, placenta, bone marrow, peripheral blood, as well as germinative tissues and cells.
Cryopraxis Cryobiology is a company dedicated to the collection, transportation, processing, freezing, long-term storage and biologic analyses of stem cells in the blood of the umbilical cord, placenta, bone marrow, peripheral blood, as well as germinative tissues and cells. Cryobiology may be defined as the science and group of technologies relating to the behavior and physiologic integrity of cells and biologic tissues when submitted to ultra low temperatures.
As a Bank of Blood of Umbilical Cord and Placenta for Autologous use, Cryopraxis stands out as the first and major company in Latin America. Cryopraxis was the first umbilical cord blood bank to obtain certification by ANVISA, the National Health Surveillance Agency.
An excellent company in its branch, counting on a staff with more than 500 direct and indirect professionals, as scientists, physicians, pharmacists, nurses, biologists, administrators and managers with the highest technical and scientific level, the great majority of which are Masters and PhDs.
The Master Unit of Cryopraxis is located in the Biotechnology Center of Rio de Janeiro - BioRio, at Federal University of Rio de Janeiro contributing to the creation of human resources and the development of new technologies. Cryopraxis usually invests in creating human resources, research and development, innovation, and it results in better and more efficient laboratorial procedures — more safety for our clients.
Technical operations by Cryopraxis are extended throughout the Brazilian territory and some European countries, United States and Canada.
Criopraxis
Biotechnology Center of Rio de Janeiro - BioRio, UFRJ
Rio de Janeiro
Phone (+5521) 2141-7777
Site http://www.cryopraxis.com.br
Sugar Cane and Ethanol
In order to grow along with that demand, Brazil and the countries that are preparing themselves to take advantage of the same opportunity – in particular the United States, China and India, which accounted for 80% of the world’s output in 2005, according to the Renewable Fuel Association — must find a way to produce more ethanol without using up all the planet’s tillable area.
Unicamp Innovation has been following the world’s movement towards ethanol and other fuels produced from biomass; and the recognition of the international media – recent – of Brazil’s leadership in the area. This edition brings part of what we have published on the theme, as well as new articles, such as those about two small businesses financed by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (São Paulo State Research Foundation, Fapesp) that operate in the sugar and alcohol industry.
The State University of Campinas (Unicamp), in the city of Campinas, about 100 km (about 62 miles) from the capital city of the State of São Paulo, is Brazil’s second largest university according to academic standards. Celebrating its 40th anniversary in 2006, it boasts impressive numbers: nearly 30,000 students, almost half of which in Graduate courses, about 1,800 professors (93 percent of them PhDs), 20 teaching and investigation units, more than 50 Undergraduate courses, over 110 Graduate courses. Each year almost 1,300 Master’s Degree theses and nearly 750 PhD dissertations are defended. In its July, 2000 issue, Wire magazine described Unicamp as “Brazil’s answer to MIT,” saying that “it houses the nation’s number one computer science program and churns out future digerati who needn’t look far for a job.”
EXTRACTA
 EXTRACTA Moléculas Naturais S.A. is a Brazilian R&D service provider to BioPharma, Veterinary, Cosmetics and Agro industries, offering state-of-the-art HTS screening against client targets and isolation of New Chemical Entities from Brazilian biodiversity.
EXTRACTA Moléculas Naturais S.A. is a Brazilian R&D service provider to BioPharma, Veterinary, Cosmetics and Agro industries, offering state-of-the-art HTS screening against client targets and isolation of New Chemical Entities from Brazilian biodiversity.EXTRACTA´s own BANK OF CHEMICAL BIODIVERSITY® is the largest, constantly growing collection of ready-to-screen compounds derived from Brazilian biodiversity within the legal framework of the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity.
A growing library of plant extracts and their fractions totaling nearly 40,000 samples readyfor screening against bioassays in a 96-well plate format. The library contains nearly5,000 plant species professionally collected in the Atlantic Rain Forest and Oriental Amazon.This highly diversified material generated close to 11,000 different crude extracts obtainedfrom plant parts and close to 29,000 fractions that together constitute the basis for everyscreening exercise
EXTRACTA offers partners uncomplicated access to this immense chemical reservoir with comprehensive, worldwide IP arrangements (no IP stacking).
Current Collaborations: GlaxoSmithKline, Genzyme Corporation and Natura (largest cosmetic/phytoremedies concern in Brazil.
EXTRACTA Moléculas Naturais S.A.
Av. 24 s/n Quadra A Lote 6 e 7 - Cidade Universitária
Rio de Janeiro
Phone (+5521) 3867-5608
Site: http://www.extracta.com.br
Children´s Machine
 The brazilian government received the first 50 2B1 ("to be one") laptops yesterday (november 27), targeted to resources research and development by R&D centers and universities. In january 2007, 550 laptops will be sent to Ministry of Education to pilot projects among the students.
The brazilian government received the first 50 2B1 ("to be one") laptops yesterday (november 27), targeted to resources research and development by R&D centers and universities. In january 2007, 550 laptops will be sent to Ministry of Education to pilot projects among the students.The Children's Machine, or 2B1, is a proposed inexpensive laptop computer intended to provide every child in the world access to knowledge and modern forms of education. It was previously known as the $100 Laptop. The laptop is being developed by the One Laptop per Child (OLPC) trade association. OLPC is a U.S. based, non-profit organization created by faculty members of the MIT Media Lab to design, manufacture, and distribute the laptops.

The computers will be rugged and use Linux for their operating system. Mobile ad-hoc networking may be used to allow many machines Internet access from one connection over the OLSR wireless protocol. The pricing goal is currently expected to start at around US$135-140 and reach the US$100 mark in 2008. The laptops will be sold to governments and issued to children by schools on a basis of one laptop per child. Brazil, Argentina, Nigeria and Lybia are the first countries to receive the 2B1 laptops.
Sugar-based plastic
Bioplastics are a form of plastics derived from plant sources such as sugar cane, soy bean oil and corn starch rather than traditional plastics which are derived from petroleum. This is regarded as a much more sustainable activity, as it relies considerably less on fossil fuel imports and produces less greenhouse emissions, producing between 0.8 and 3.2 tonnes of carbon dioxide less per tonne of bioplastics compared to the same weight in petroleum-based plastics. Many bioplastics are truly biodegradable and will degrade in commercial compositing units. Some bioplastics will even biodegrade in the less aggressive conditions of a home compost heap. However, bioplastics can also be formulated to be durable.
This development is closely associated with the long term activity of sugar and alcohol production in Brazil, which is based on the natural endowments of soil, climate and geographical extension that favors sugar cane cultivation.
This notwithstanding, the emergence of the bioplastic industry was only possible because of a specific government scheme to build research capacity and knowledge production in biotechnology which also stimulated cooperation between the public and the private sector.
14 Bis - 100 Years

The 14-bis, also known as Oiseau de proie (French for "bird of prey"), was an early fixed-wing aircraft designed and built by Brazilian inventor Alberto Santos-Dumont. On November 12, 1906, in Bagatelle, France, it performed the first publicly witnessed unaided flight by a heavier-than-air aircraft. Earlier flights, such as that made by the Wright Brothers had required favourable wind directions, catapults or other such devices to take off.
Conception, development, and initial tests
In June of 1905, Gabriel Voisin tested a glider by having it towed by a fast boat down the Seine. The glider's wing configuration was made up of Hargrave cells, a box-kite-like structure that allowed for great lift and structural strength with minimal weight. Voisin was towed into the air and flew for over 500 feet as the boat pulled him and his aircraft. In the aviation-crazy Paris of the early 1900s, this established the Hargrave cells as a configuration to be developed into heavier-than-air aircraft, not simply into kites. Santos-Dumont lived in Paris at the time, and was by then one of the most active "aeronauts" in Europe, having developed a long series of dirigibles that displayed unparalleled agility, speed, endurance, and ease of control.
During late 1905 and early 1906, French aviation authorities, seeing the rapid development in aviation at the time, offered prizes for the first heavier-than air machines to be flown for 25 meters and for 100 meters. Ferber, a captain in the French Army, was experimenting with gliders and kept in touch with Chanute and with the Wright brothers. Voisin teamed up with Louis Bleriot to develop the boat-towed glider into a fixed-wing aircraft.
At around that time, while watching the Cote D'Azur speedboat races, Santos-Dumont noticed that Antoinette-type engines, made by Levavasseur, offered great power and were quite lightweight.

Putting all this together, Santos-Dumont designed and built a Hargrave-cell biplane powered by an Antoinette engine. This was originally done in secrecy, only known to his team of builders and craftsmen. The wings were at the very back configured in a dihedral, each wing containing three cells. The 24 hp Antoinette sat between the wings, with the pilot's compartment immediately ahead (where the pilot stood), and with the pusher-propeller immediately behind. A movable cell at the nose, actuated by cables originally manufactured for church-tower clocks, allowed for steering and altitude adjustments. This forward-mounted-mini-wing layout would later come to be called a "canard" (after a Bleriot aircraft of the same layout was said to look like a duck. This name is still used to describe aircraft with wing-like surfaces placed near the nose, whether or not they are duck-like). The structures of the Santos-Dumont biplane were made of bamboo, with Japanese silk surfaces, and joints made of aluminum, a very exotic material at the time.The aircraft was transported from Neuilly, where it was built, to Bagatelle, where it could be tested. In order to simulate flight-like conditions, Santos-Dumont attached the aircraft to the belly of his latest dirigible, the Number 14. Due to this configuration, the plane came to be known as 14-bis. The forces imposed by the aircraft pulled at the dirigible in dangerous ways, nearly tearing it and allowing for limited control. The danger of such tests caused Santos-Dumont and his team to quickly abandon them, although some constructive information was obtained that led to adjustments in the balance and weight placement of the plane.Santos-Dumont then connected a steel cable to the tops of two tall poles, one taller than the other. The aircraft was hung by a rope and attached by a pulley to the steel cable. It was then pulled by a donkey until it rested by the taller pole, and then released and allowed to slide down the cable towards the lower pole. In this manner, the center of gravity of the aircraft was established and adjusted, and much was learned about its stability. (Photographs of these tests show the vehicle being pulled up along the cable by the donkey back to the higher position. This gives the appearance that the plane was tested while being pulled by a donkey, which is not accurate).
By August 1906, the aircraft was transported back to Bagatelle, where Santos-Dumont performed what we would today call fast-taxi tests. The engine was found not to be powerful enough to safely reach flight speeds, and was replaced by a 50 hp Antoinette, a V-8 design capable of 1,500 rpm. Early September saw greater speeds in ground tests, as well as a minor accident. On the September 7, 1906, the wheels left the ground during an extremely quick hop.Announcements were made about Santos-Dumont trying for all the aeronautics prizes. Crowds and aviation authorities gathered on the morning of the September 13, 1906. Not all the cylinders were firing during an initial takeoff attempt, but quick repairs allowed for the second run to result in a 13-meter (43-foot) hop, an altitude of about 1 meter having been reached. This did not qualify for the prizes, but earned Santos-Dumont a great deal of attention.The 14-bis landed at a high angle of attack, and the propeller at the back struck the ground. Repairs were undertaken. On the 23 October, after a series of engine tests and high-speed ground runs (one of which ended as one wheel came loose, but this was quickly fixed), Santos-Dumont finally pulled the 14-bis into the air. The aircraft flew for over 200 feet at an altitude of about 10 feet. This earned Santos-Dumont the first of the aviation prizes, 3,000 francs for a 25-meter-or-greater flight.
The plane required more repairs, as the landing had again damaged it, and Santos-Dumont announced that he should be ready to attempt the 100-meter prize on November 12. The 14-bis was repaired, and ailerons were added to the middle of each outermost wing cell (similar to the aileron layout later used in the famous Curtiss Model D Pusher). These ailerons were actuated by cables attached to the pilot's flightsuit at the shoulders. Movement of the shoulders thus actuated roll control, similarly to the hip-movement roll-actuation control on the Wright Flyer.
On the morning of November 12, 1906, the crowds gathered. In a surprise to nearly all there, Voisin also brought a biplane that he and Bleriot has built, and also powered by an Antoinette. Voisin made several takeoff attempts, until one of them damaged the vehicle such that it could not be tested further before being extensively repaired.

As Santos-Dumont allowed the 14-bis to run down the field, a car drove alongside, and Henry Farman would drop a plate out of the car each time he observed the wheels of the plane to leave the ground or to touch down again. The first attempt saw a flight of 40 meters, and the second saw two brief flights of 40 and 50 meters. A hurried landing after this second attempt (rushed due to the proximity of some trees) damaged the wheel axles, and these were fixed during a lunch break. In the afternoon, further flights were of 50 meters and then 82 meters. As the sun set, Santos-Dumont attempted one more flight. In order to ensure he would not hit spectators, who by this time were present all over the field, he flew at an altitude of 4 meters. After 22 seconds, he cut the engine power and glided into a landing. He had flown for 220 meters, or over 700 feet, qualifying for the second aviation prize offered for heavier-than-air-aircraft, 1,000 francs for a flight of 100 meters or more.
Specifications (14-bis)
General characteristics
- Crew: one pilot
- Capacity: one
- Length: 9.70 m (31 ft 10 in)
- Wingspan: 11.20 m (36 ft 9 in)
- Height: 3.40 m (11 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 52 m² (560 ft²)
- Empty weight: ? ()
- Loaded weight: 300 kg (660 lb)
- Powerplant: 1× AntoinetteV-8 , 37 kW (50 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 32 km/h to 43 km/s (25 mph/1.1.)
- Range: >220 m (demonstrated) (>720 ft)
- Wing loading: 5.7 kg/m² (1.2 lb/ft²)
- Power/mass: 0.12 kW/kg (0.075 hp/lb)
Oil Sorb

Oil Sorb is a natural product, non toxic, with high standards for oil absorbance, greases and others organic composites.
The Oil Sorb absorbent line are used in normal conditions when oil is spread or emitted, or when an oil spill situation occurs. The HydroClean line of Oil Sorb absorbent is prepared to prevent environment damages or risks to people security.
Many important industries have already used and perceived the benefits of the Oil Sorb as an ally to struggle against greasy and oil substances. The main vertical markets that uses Oil Sorb line are from oil & gas, chemistry, mines, energy and food & beverages industries. Others great users are from the public sector, as water effluents treatment.
 Developed by engineer Jader Martins from Federal University of Ouro Preto, the Oil Sorb is a hidrophobic mineral sponge driven from vermiculite, a non toxic mineral which expands 20 times with the application of heat (1000ºC ~ 1832ºF) producing a filament that can absorb 5 times its weight in oil, grease and fat.
Developed by engineer Jader Martins from Federal University of Ouro Preto, the Oil Sorb is a hidrophobic mineral sponge driven from vermiculite, a non toxic mineral which expands 20 times with the application of heat (1000ºC ~ 1832ºF) producing a filament that can absorb 5 times its weight in oil, grease and fat.There is a plenty of vermiculite in Brazil (Piaui, Goias, Paraiba and Bahia), a thermic and acoustic isolant mineral used in the production of light bricks and now being used to clean waterstrains and rivers. Oil Sorb (US$ 5.00/Kg) is cheaper than the peat imported from Canada (US$ 25.00/Kg) to absorb oil from waterfalls.
The residues obtained with Oil Sorb utilization after oil absorbance can also be used in Portland Cement processing and fabrication. It is possible because this residues contains two basic components: The oil, that generates heat and the Oil Sorb itself, made by a substance commonly used in cement production.
Hydroclean
Belo Horizonte, MG
Phone: + 55 31 3264-5900
Email: hydroclean@hydroclean.com.br
Website: www.hydroclean.com.br
Claro IdeiasTV
 IdeiasTV is a Mobile TV service launched (02) by Claro1 in a parternship with MobiTV2. There are eight traditional TV channels (CNN, Cartoon Networks, A&E, History Channel, Discovery, Nickelodeon, Bloomberg, Maxx Esportes), Fashion TV and one specially made for mobiles (ESPN Mobile). From the ten channels only CNN, Fashion TV and Maxx Sports are not in portuguese.
IdeiasTV is a Mobile TV service launched (02) by Claro1 in a parternship with MobiTV2. There are eight traditional TV channels (CNN, Cartoon Networks, A&E, History Channel, Discovery, Nickelodeon, Bloomberg, Maxx Esportes), Fashion TV and one specially made for mobiles (ESPN Mobile). From the ten channels only CNN, Fashion TV and Maxx Sports are not in portuguese. Avaliable at the first momment only to the Nokia models 3250 (US$ 600.00), N80 (US$ 1,000.00), E63 (US$ impratical) and Palm Treo 650 (US$ 800.00) – the reasonable price for a mobile in Brazil is US$ 200.00. The service has already two competitors, Vivo Play 3G and Tim TV Access.
Pre-Paid and Post-Paid clients have access to the application which is downloaded from Claro WAP Portal (wap.claro.com.br). Claro created three different subscriber plans: US$ 1.50/day, US$ 5.00/week or US$ 15.00/month. And US$ 17.50 (10Mb); US$ 40.00 (40Mb) or US$ 70.00 for unlimited download.
The service is too much expensive to the brazilian average pocket and not even a brazilian news channel (Globo International, Globonews or Band News) is among the ten ones. In spite of the streaming MobiTV service, if a regular TV-on-a-chip could be part of a US$ 200.00 model, at least 21 million Claro users could watch our commercials, soap operas, TV series, football matches, educational programs on the bus, trains, undergrounds and everywhere.
1 Claro (Telecom Americas) is the brazilian subsidiary of America Movil. America Movil (Public, NYSE:AMX) is a publicly traded wireless communications company that provides services to over 93.3 million wireless subscribers in Latin America as of December 31st 2005. The company has been a venture of Carlos Slim Helu. World headquarters is located in Mexico City, Mexico. It was ranked number 1 Information Technology company in 2005 by the Business Week magazine.
2 MobiTV formerly called Idetic, was founded in 1999. The company's products incorporating the technology are ReachINTERNET, for Web acceleration and optimization; ReachWiFi, a multinetwork bridge; and ReachTV, a media bridge. Through its service, wireless service providers are able to feed live TV broadcasts to their subscribers' cell phones. MobiTV works with such tech vendors as Hewlett-Packard, Siemens, and Sun Microsystems.
Treetap
 The Treetap brand and design born as a way of adding value to raw material known as vegetal leather. Manufactured in Amazon Forest communities from the latex, this technology became an environmentally sustainable way of increasing region's labor income. Designed by Beatriz Saldanha and Tatiana Pinho, manufactured by Couro Vegetal da Amazônia.
The Treetap brand and design born as a way of adding value to raw material known as vegetal leather. Manufactured in Amazon Forest communities from the latex, this technology became an environmentally sustainable way of increasing region's labor income. Designed by Beatriz Saldanha and Tatiana Pinho, manufactured by Couro Vegetal da Amazônia.Couro Vegetal da Amazônia S.A.
Rua Visconde de Pirajá 499 sobre loja.
Rio de Janeiro
phone (+5521) 24331697
Site http://www.amazonlife.com/
Vetor Zero
 Vetor Zero is a special effects and digital animation company that has been in business for over 18 years, servicing clients in Brazil and world wide with top-level animation work, creative input and technical ingenutity.
Vetor Zero is a special effects and digital animation company that has been in business for over 18 years, servicing clients in Brazil and world wide with top-level animation work, creative input and technical ingenutity. At the forefront of animation and digital effects, Vetor Zero help their clients realize their visions, strengthen thier brands and stand out visually. As a result, their works have been highly regarded and widely rewarded both locally and overseas in all the major advertisement and animation festivals worldwide.
At the forefront of animation and digital effects, Vetor Zero help their clients realize their visions, strengthen thier brands and stand out visually. As a result, their works have been highly regarded and widely rewarded both locally and overseas in all the major advertisement and animation festivals worldwide.From TV packages for Brazilian Networks, to the far out concepts and graphics for Chevrolet, Vector Zero's clients so far include Adams, Audi, Brahma, Coca-Cola, Colgate, Fiat, Ford, Mastercard, Michelin, Nestea, Nissan, ONU, Pepsi, Petrobras, Peugeot, Ruffles, Siemens, Sundown, Telmex, TIM, Toyota, Trakinas, Trident, Unilever, Volkswagen and Wall Mart.
10 Cannes Lions (3 Gold)
1993 - "Worms" - Bronze
1995 - "Spoons" (Kibon) - Silver
1996 - "Ants" (Philco) - Gold
1996 - "Ants with Helmet" (Philco) - Bronze
1998 - "Leds" (Gradiente) - Gold
1998 - "Tree" (Jovem Pan) - Bronze
2000 - "Baby" (Zip Net) - Bronze
2003 - "Flea" (Purina Tratto) - Bronze
2004 - "Together" (Zoo Buenos Aires) - Bronze
New York Festivals
1997 - "Mosquito" (Antena 1) - Gold
1997 - "Leds" (Gradiente) - Gold
2000 - "Baby" (Zip Net) - Gold
2004 - "Fish" (TV Animation Computer) - Bronze
Annecy - Festival International du Film D'Animation (France)
2002 - "Turtle" - Advertising Film Award
Vetor Zero
Phone: +55 (11) 3709.2222
Site: http://www.vetorzero.com/
TIM Home
2. Disk *333 from inside your home.
3. Now you can make every call from your mobile at your homezone to any fixed phone with local fixed shares.
Homezone GSM localization is the use of Multilateration or 'trilateration' to determine the location of GSM mobile phones, usually with the intent to locate the user. You call the *333 and the 'Trilateration' thing begins.
 Trilateration is a method of determining the relative positions of objects using the geometry of triangles in a similar fashion as triangulation. Unlike triangulation, which uses angle measurements (together with at least one known distance) to calculate the subject's location, trilateration uses the known locations of two or more reference points, and the measured distance between the subject and each reference point. To accurately and uniquely determine the relative location of a point on a 2D plane using trilateration alone, generally at least 3 reference points are needed.
Trilateration is a method of determining the relative positions of objects using the geometry of triangles in a similar fashion as triangulation. Unlike triangulation, which uses angle measurements (together with at least one known distance) to calculate the subject's location, trilateration uses the known locations of two or more reference points, and the measured distance between the subject and each reference point. To accurately and uniquely determine the relative location of a point on a 2D plane using trilateration alone, generally at least 3 reference points are needed. Standing at B, you want to know your location relative to the reference points P1, P2, and P3. Measuring r1 narrows your position down to a circle. Next, measuring r2 narrows it down to two points, A and B. A third measurement, r3, gives your coordinates at B. A fourth measurement could also be made to reduce error. And that's why Bin Laden could not have a mobile phone!
Standing at B, you want to know your location relative to the reference points P1, P2, and P3. Measuring r1 narrows your position down to a circle. Next, measuring r2 narrows it down to two points, A and B. A third measurement, r3, gives your coordinates at B. A fourth measurement could also be made to reduce error. And that's why Bin Laden could not have a mobile phone!The beautiful thing about innovation is that it puts all these physics, mathematics and difficult things toghether in my hands to simply order a pizza!
1TIM (TIM Participacoes - Public, NYSE:TSU) is a wireless provider in Brazil. The Company offers value-added services, including short message services or text messaging, multimedia messaging services (MMS), push-mail, Blackberry service, video call, turbo mail, wireless application protocol (WAP) downloads, Web browsing, business data solutions, songs, games, television access, voice mail, conference calling, chats, and other content and services. On March 16, 2006, the Company acquired all of the share capital of TIM Celular S.A.
Siemens Global Network of Innovation

Networks are the talk of the town. Scientists, economists, politicians and philosophers all speak about networks. When people speak about networks, they are always actually speaking about the special relations that make something what it is.
Thus the effectiveness of a medication is based on its molecular components and the special configuration in which these relate to each other. Decisive are not just the "ingredients" but to a large extent the special position of the building blocks in relation to each other.
Siemens is about to win the Finep1 Technological Innovation Prize in Brazil regarding to its Global Network of Innovation.
This can be translated as the company's innovative strength, its innumerous business activities and, of course, its global network, composed of more than 400,000 employees in 190 countries.
Networks describe both complex structures and the special position of the individual elements as a system of relations. Elements such as nodes and links, representing in such case companies and business relationships, can be build and turned on or turned of to accomplish unparalled actions such as new products, process and services.
Siemens acts, like the catalyst - as we speak about chemical complex structures, of this complex structure. In chemistry, a catalyst (Greek: καταλύτης, catalytēs) is a substance that accelerates a reaction, without itself being consumed or changed. In this case the catalyst, or Siemens, change and change a lot, learning with the business environment and participating in the process of innovation, research and entrepreneurship of people, universities, research institutes and companies around it.
Our social world is an intricate universe of social, economic and political relations. Our world is complex. To be sure, this is not a new phenomenon. But it is a fact that the complexity of the world around us is becoming increasingly difficult for the individual to grasp. Companies, like Siemens, are drowning in the short-sighted probabilities of their own decision-making structure. It is becoming increasingly difficult to find a basis for sensible reforms, and new groups of clients are increasingly difficult to reach in a fragmented market. Today's formula is to became one of the nodes or became the catalyst.
 Siemens is strongly represented in Brazil. The Company's first activities in the country date back to 1867, with the installation of the first telegraph line between the states of Rio de Janeiro and Rio Grande do Sul. In 1895, in Rio de Janeiro, it opened its first office and ten years later the Company was founded in Brazil. Siemens is among the leading companies in Brazil's electric and electronic sector, with business activities in the areas of Information and Communications, Automation and Control, Medical, Power, Transportation and Lighting. In Brazil, the Company possesses 10,305 employees, seven research and development centers and sixteen manufacturing facilities, some of which occupy a prominent position within our worldwide organization. Such is the case with the Curitiba plant, a global export center of the HiPath 1000 and 4000 corporate communication platform, marketed worldwide by Siemens.
Siemens is strongly represented in Brazil. The Company's first activities in the country date back to 1867, with the installation of the first telegraph line between the states of Rio de Janeiro and Rio Grande do Sul. In 1895, in Rio de Janeiro, it opened its first office and ten years later the Company was founded in Brazil. Siemens is among the leading companies in Brazil's electric and electronic sector, with business activities in the areas of Information and Communications, Automation and Control, Medical, Power, Transportation and Lighting. In Brazil, the Company possesses 10,305 employees, seven research and development centers and sixteen manufacturing facilities, some of which occupy a prominent position within our worldwide organization. Such is the case with the Curitiba plant, a global export center of the HiPath 1000 and 4000 corporate communication platform, marketed worldwide by Siemens.Don't you think that the Global Network of Innovation deserves this prize?
1 Finep - National Agency for Financing Studies and Researches, is a part of the Ministry of Science and Technology (MCT) created in 1986 specifically for directly promoting and funding R&D&I in Universities and now directly to Private and Public Companies with Federal Government sources.
Coca-Cola Brazil Clean Water

Water. I do not know why, but on the last few weeks I am thinking about the waterways and rivers of my country. It might be the effects of the "What The Bleep do we Know?" movie and from the Masaru Emoto's "Life of Water"1 experiences. Just like a lot of enterprises, and everyones depends of water, Coca-Cola Brazil is helping to improve its quality trought technological innovation and better environmental pratices.

Coca-Cola Brazil2 is one of the beverage company's largest operations in Latin America, providing drinks for thirsty Brazilians through a network of 39 bottling plants that are operated by 18 independent groups working under a franchise system that employs about 25,000 people. Under this business model, the franchisees agree to produce all Coca-Cola products from a supply of concentrates and then bottle and distribute them.
The Cempre (Enterprise Commitment for Recycling), created in 1992 by Coca-Cola and a group of companies, acts in technological research, projects orientation and information diffusion on management of solid residues and recycling, in partnership with reputation entities, as the Institute of Technological Research of São Paulo (IPT).

Besides all soft-drinks brands Coca-Cola Brazil produces bottled mineral water too, the Bonaqua brand, making it from better filtering and environmental managing Systems. A friend of mine that works in the brazilian company swear that a lot of patogenic and natural diseases are interrupted by the filters, chemicals and an intricated industrial process developed by Coca-Cola with a large network of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SME) and University research after a long way of 64 years (1942) of technical achievements in our country.
Coca-Cola Brazil uses billions of liters of water per year to manufacture its products. And from the point of view that water is a common good, Coca-Cola Brazil created the Clean Water Program. To have an idea of the dimension of this program, it is enough to say that each year 1 billion of liters of water is saved, the sufficient to supply, annually, a city with 25 thousand inhabitants. This says that the consumption average is of 2,4 liters of water for 1 liter of drink, one of the minors of the world. And we are becoming each year more efficient, thanks to the awareness and to the modern methods of management of the use of water. But the rationalization is not the only objective. The Clean Water Program also treats 14 billion liters of water used in its production process, that in turn are returned to the rivers and lakes to preserve and to improve the quality of the same ones. Coca-Cola Brazil only gives an example of that it is possible to make, so that other company-citizens make the same. The future is thankful.
1 In The Secret Life of Water, bestselling author Masaru Emoto guides us along water’s remarkable journey through our planet and continues his work to reveal water’s secret life to humankind. He shows how we can apply its wisdom to our own lives, and how, by learning to respect and appreciate water, we can better confront the challenges that face the twenty-first century—and rejuvenate the planet.
2 Yes, indeed The Coca-Cola Company has assumed a national position in our contry and begun to use 'Brazil' on it's name and made a little change on it's logo (the yellow & green flag) becoming the first affiliate of the multinational company to have a customized look from the universal brand.
Deflor Bioengineering
 DEFLOR was founded in 1984 to work in environmental protection and pest control. Its activities developed into hydraulic dam cleaning and the recovery of degraded areas. At present DEFLOR manufactures plant and coconut fiber anti-erosion biodegradable blankets and sediment retainers which are sold domestically and internationally. All products abide by the ASTM - American Society for Testing and Materials - international standards. The 15,000 m² manufacturing plant is located in Contagem, MG.
DEFLOR was founded in 1984 to work in environmental protection and pest control. Its activities developed into hydraulic dam cleaning and the recovery of degraded areas. At present DEFLOR manufactures plant and coconut fiber anti-erosion biodegradable blankets and sediment retainers which are sold domestically and internationally. All products abide by the ASTM - American Society for Testing and Materials - international standards. The 15,000 m² manufacturing plant is located in Contagem, MG.DEFLOR has a highly qualified technical staff, including experts to design specific projects for each customer like the Anti-erosion Biodegradable blankets, Sediment Retainers, Erosion and Sediment Control and Environmental Solutions for Degraded Areas and Poluted Waterways.
 The Bermalonga® type sediment retainers may be used to retain, conduct and confine oil and suspended material leakage into a desired site. Those special sediment retainers are widely applied in engineering works. They are light, easily managed, transported, installed and stored. Produced with DEFLOR technology, it is extremely strong and has been successfully used to fill erosion pits, deep erosion gullies, on slope and erosion gully surfacing.
The Bermalonga® type sediment retainers may be used to retain, conduct and confine oil and suspended material leakage into a desired site. Those special sediment retainers are widely applied in engineering works. They are light, easily managed, transported, installed and stored. Produced with DEFLOR technology, it is extremely strong and has been successfully used to fill erosion pits, deep erosion gullies, on slope and erosion gully surfacing.Waterway, canal and hydraulic resevoir recovery and protection is essential to avoid margin undermining, erosion and silting, all of which affect the environment, the community and enterprises. Choosing the most efficient and safest measure among existing products and technology depends on expert knowledge like the one developed by the DEFLOR staff.
DEFLOR
Belo Horizonte - Minas Gerais - Brazil
E-mail :deflor@deflor.com.br
Phone 55 31 3284-5622
Fax 55 31 3284-5688
Dye-cells

The sunlight that reaches the earth’s surface represents a constantly renewable source of energy. Countries whose territories include extensive areas of land near the equator can develop and exploit the abundant sunlight that bathes their land as an alternative source of renewable energy. As solar technology advances, such efforts carry significant environmental and economic benefits.
Brazil is the fifth-largest country in the world in terms of territory, covering more than 8,500,000 square kilometers. Almost 80 percent of this land lies in the tropics between the equator and the Tropic of Capricorn.

Using natural pigements extracted of fruits as blackberry, jabuticaba and caulker (common in the region of Patagonia, in the South America), scientists of the Chemistry Institute (IQ) of the University f Sao Paulo had developed a new technology for the production of cells capable to convert the solar light into electric energy, the Dye-cells® calls - solar cells of thin layer.
Compared with the conventional systems, that they use as substance cousin the silicon, the process presents advantages as the cost of production - esteem in about 30% 50% minor - and the use of materials that do not attack the environment.
In the laboratories of the IQ already exists a 10x10 cm Dye-cell®, with the appearance of a transparent glass, that demonstrate the efficiency of the technology. Andres Sarto Polo, currently on doctoral at the Institute, explains that the system uses as semiconductor the titanium dioxide (TiO2). "This substance is used in the industry in dental creams, inks etc. For being white, it does not absorb the visible light and it needs a pigement to absorb the solar light, that can be extracted from fruits."
In tests made with caulker and jabuticaba, the researchers had obtained to reach powers around 1,5 to 2 miliwatts for squared centimeter (cm2). The control experiments come being carried through in small solar cells that presents an active area of 1/2 cm2. According to Polo, already if it knows that the system with natural pigements is capable to convert the energy proceeding from sun into electricity with efficiency around 1% to 2%.
The next steps to the studies, in accordance with Polo, will be to verify the time of useful life of the cells and the use of different composite.
USP Chemistry Institute
São Paulo - SP
Telephone: (+5511) 3815.3257 / 3091.3839
Website: http://www2.iq.usp.br
Moscamed Biofactory

Fruit farmers of Brazil and of the world have been granted assistance in fighting the worst pests that affect their crops: fruit flies, scientific name Ceratitis Capitata. The Biofabrica Moscamed Brasil factory, in the city of Juazeiro, in the northeastern Brazilian state of Bahia is becoming the first to produce sterile fruit flies to help combat the plague.
Sterile insect technique is a method of biological control, whereby millions of sterile insects are released. The released insects are normally male as it is the female that causes the damage, usually by laying eggs in the crop. The sterile males compete with the wild males for female insects. If a female mates with a sterile male then it will have no offspring, thus the next generation's population is reduced. Repeated release of insects can eventually wipe out a population, though it is often more useful to consider controlling the population rather than eradicating it.
The biofactory, whose target is to produce 200 million sterile male flies per week, is born with the perspective of being an exporter. According to agronomist Antonio Nascimento, the Moscamed Brasil technical and scientific consultant, Spain and South Africa are potential markets for future exports of natural pest control.

The researcher explains that research took ten years. Work by the Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (Embrapa), universities and research institutes was necessary to reach the biofactory. "This is truly interdisciplinary and inter-institutional team work," he said. The technology for production of sterile fruit flies is already used in other countries, but not in Brazil, the third largest world producer of fruit. The biofactory is the first of its kind.
According to him, the sterile insect technique will reduce the use of pesticides in Brazilian fruit farming and will represent a positive impact to the environment. "On the other hand, this technology will contribute to the production of more healthy fruit, as well as increasing the Brazilian competitiveness on the foreign fruit market, marked by greater and greater demands with regard to food safety," pointed out Nascimento.
Biofábrica Moscamed
Quadra D13, Lote 15 - Distrito Industrial do São Francisco
Juazeiro - Bahia
Telephone: (+5574) 36125399
Site: www.moscamed.org.br
DryWash

Water (in its pure form) is a tasteless, odorless substance that is essential to all known forms of life. Our planet Earth could be called Water because 2/3 of it is covered by this precious substance that even make 75% of your body. Civilization has historically flourished around rivers and major waterways. Due to overpopulation in several regions of the world, the safe water supply is inadequate as of the year 2006 (and decades prior). Much of the world’s water systems are also aging and in need of major infrastructure improvements.
Current forecasts are that two thirds of the planet will have insufficient water by 2025, when it will be the natural resource more disputed at the majority of countries. In Brazil water in abundance exists, but it also exists the wastefulness and the compromizing of the sources.
 With a hose not very opened, 216 liters of water are spent in 30 minutes of laudering. The DryWash founder, Lito Rodriguez, set out to reverse this trend when he created the company in 1994. Armed with a solid management team and a unique product, he prepared to change the status quo and run a small business that has a compromissing with the future.
With a hose not very opened, 216 liters of water are spent in 30 minutes of laudering. The DryWash founder, Lito Rodriguez, set out to reverse this trend when he created the company in 1994. Armed with a solid management team and a unique product, he prepared to change the status quo and run a small business that has a compromissing with the future.
The main advantage DryWash holds over its rivals is an innovative line of vehicle cleaning solutions that have yet to be replicated with the same degree of quality and efficacy. As its name implies, the company has created products that wash every part of a car without the use of water. Aside from the clear environmental benefits, such as the estimated 450,000,000 liters of water DryWash saved in its first ten years, the superiority of the products themselves is still unmatched.
The original cleaner is a small pad that uses organic Carnauba wax local to Brazil which efficiently removes dirt from the vehicle’s surface with no harmful chemicals. This technology is so successful that it has created significant international interest, allowing DryWash to expand its services into Mexico, Portugal and Australia in addition to the fifty franchises and several mall units it already maintains.
Within Brazil, the company is creating a pro-business environment in an industry dominated by informality and illegal practices. The management team’s focus on operating the most efficient and professional business possible has paid off. New laws have greatly increased the penalty of buying and reselling products illegally, so foreign corporations prefer working with DryWash because of their prospects for future stability and growth. In addition, customers are drawn to the quality of the service and product, generating consistent press coverage and causing sales to increase exponentially. DryWash beat its own sales expectations of $2.4 million by generating $2.7 million in revenue in 2005. The company is continually adjusting its prospects upward, now to $5.46 million in sales for 2008. The DryWash system proved to be so popular, the office began getting calls from clients asking if the products could be used on planes and helicopters, prompting the founders to create a separate branch called DryWash Air.
The company has further improved its efficiency by creating management software that standardizes operations among franchises and car wash units. DryWash is now performing market research to expand its operations into the US with “Eleva,” a new, comprehensive line of sustainable cleaning products.
DryWash
Sao Paulo, SP
e-mail: international@drywash.com.br
website: http://www.drywash.com.br
SARAH Network of Rehabilitation
 The SARAH Network, one of the largest Rehabilitation, Orthopedic and Neuropsychology Networks in the world.
The SARAH Network, one of the largest Rehabilitation, Orthopedic and Neuropsychology Networks in the world.It is an institution dedicated to rehabilitation and treatment of malformations, traumas, locomotor system diseases and neurodevelopmental problems. Its purpose, then, is to provide specialized rehabilitation services to every strata of the population, regardless of class, race, socio-economic background, religion or gender.
The SARAH Network of Rehabilitation Hospitals is comprised of six hospital units located in Brasilia (DF), Salvador (BA), São Luis (MA), Belo Horizonte (MG), Fortaleza (CE) and Rio de Janeiro (RJ).
Each hospital in the Network is place a for perpetuating and perfecting the principles, concepts and techniques consolidated over time by the Brasilia unit, which has rendered it a center of national and international reference. New technologies and methods like the SARAH Ortomovel are researched and developed by the skilled personel attented to their clients accessibility needs.
The SARAH Network restitutes, in the form of health services, the incomes taxes paid by the citizen. The financial resources that sustain all the SARAH Network hospitals come exclusively from the federal government. The funds are allocated with specific instructions determining their application in the maintenance of the Management Contract.
 Innovative initiative and the exchange of experience, in education and research, stimulating the creativity of persons and groups; “the individual is the institution” and each person represents it, answers on its behalf, and dedicates his/her life to it is the SARAH Network brand.
Innovative initiative and the exchange of experience, in education and research, stimulating the creativity of persons and groups; “the individual is the institution” and each person represents it, answers on its behalf, and dedicates his/her life to it is the SARAH Network brand.SARAH Brasilia
SMHS Quadra 501 Conj. A - Brasília - DF
Zip code: 70.330-150
Telephone (+55 61) 319 1111
Fax (+55 61) 319 1538
SARAH Ortomovel
 The Ortomovel allows that individuals carrying deficiency of mobility in the inferior members have the freedom of moving in the standing position. From a simple movement, the user of the Ortomovel can move himself of the seated position for the standing one and, thus, circulate without aid of a third. The user is safe firmly by means of security belts settled in the knees and chest, and the brakes are easily reached.
The Ortomovel allows that individuals carrying deficiency of mobility in the inferior members have the freedom of moving in the standing position. From a simple movement, the user of the Ortomovel can move himself of the seated position for the standing one and, thus, circulate without aid of a third. The user is safe firmly by means of security belts settled in the knees and chest, and the brakes are easily reached.The Ortomovel is disassembled in three parts for the transport. Because of the aluminum used in airplanes, steel and titanium, the product combines principle resistance with minimum weight. The padding of the seat and back, as well as other upholstered parts are made of injected polyurethane foam.
Designed by Antonio Cutolo, Bruno Matos, Claudio Duarte, Henry Macario, José Carlos Ferraz, Manoela Palmeiro, Paulo Fernandes, William Maria Dias, Equiphos - Technologic Research group and manufactured by the SARAH Network of Rehabilitation Hospitals.
The SARAH Network of Rehabilitation Hospitals is comprised of six hospital units located in Brasilia (DF), Salvador (BA), São Luis (MA), Belo Horizonte (MG), Fortaleza (CE) and Rio de Janeiro (RJ). The clinical conditions most frequently treated at the SARAH Network are cerebral palsy, spina bifida, traumatic brain injury, stroke, spinal cord injury, neuromuscular diseases and orthopaedic problems, among others.
Virtual Eye project

The Federal University of Pernambuco (Recife) team was the second place in the end of the world-wide Imagine Cup 2006, Microsoft's international schollar competition of technological innovation, ended up in this friday in India.
The young entrepreneurs of Trivial Team - Augusto Cesar Spinelli, Carlos Eduardo Rodrigues, Ivan Cordeiro Cardim and Madson Menezes Costa - had won more than 65 thousand representatives of more than 180 countries with the Virtual Eye project, or vEye, a portable system to aid the navigation and object identification for visual deficients.

Through two vibratory bracelets hardwired to a hand computer, the system guides the motion of blind people inside a building or in the street, signaling with vibrations where the user must follow or stop.
The team, that was the first place in the Brazilian stage of Imagine Cup 2006 , surpassed other groups of innovators from Denmark, Japan, China, Italy and Norway in India. Behind the first rank, conquered by Italians, the Trivial Team received the prize of U$S 25,000.
The theme of this year's Imagine Cup, "Imagine a world where technology enables us to live healthier lives," is a challenge to the world's top student technologists to actively contribute to the mission of improving health around the world.
Centro de Informática UFPE
Cidade Universitária - Recife
Telephone: +55 81 2126.8430
Website: http://www.ufpe.br
CardioLight Digital holter recorder
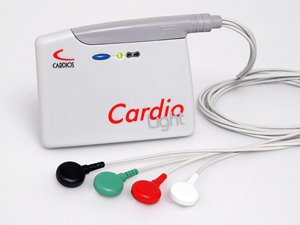 The CardioLight records the electrical activity of the heart, usually during a period of 24 hours, while patients go about their daily activities. The device weighs only 62 grams, so it is scarcely noticeable and does not interfere with the patient’s normal routine. The device is curved to fit the patient’s body snugly, and is equipped with a removable clip.
The CardioLight records the electrical activity of the heart, usually during a period of 24 hours, while patients go about their daily activities. The device weighs only 62 grams, so it is scarcely noticeable and does not interfere with the patient’s normal routine. The device is curved to fit the patient’s body snugly, and is equipped with a removable clip. Designed by Jacob Breur, Marcelo Fabiani, Fabio Pucca de Avellar Pires from DI - Design Industrial S/C Ltda. Sao Paulo, Brazil and Manufactured by Cardio Sistemas Coml. Indl. Ltda.
Designed by Jacob Breur, Marcelo Fabiani, Fabio Pucca de Avellar Pires from DI - Design Industrial S/C Ltda. Sao Paulo, Brazil and Manufactured by Cardio Sistemas Coml. Indl. Ltda.Sao Paulo, Brazil. Was Winner in the Packaging/globe packaging iF product design award 2006.
Meanwhile, Dr. Thais Russomano and her team at the PUCRS Microgravity Laboratory, Porto Alegre, Brazil are working on a research project to send the patient data through the mobile network.
The telemedicine system that is capable of remotely monitoring cardiac medical parameters in patients. It can be a valuable tool in the detection of cardiac arrhythmias. A device is attached to the patient so that the acquisition, processing, analysis and transmission of the parameters are automatically performed.
The end user of the telemedicine system, named User End Terminal (UET), is connected to a mobile terminal. This arrangement allows the UET to send information through the mobile network Short Message and Data Services, so that the cardiac information can be received in a Monitoring Center (MC). In the MC medical doctors analyze the data. At periodic intervals and in case of an alarm situation, the UET sends the waveform of the cardiac beats to the MC on a real-time basis. This feature allows the patients to stay in their houses or offices and move around freely.
NET fone Via Embratel
 Embratel1 (Public, NYSE:EMT), in partnership with NET2 (Public, NASDAQ:NETC), is launching in Brazil an international trend: Triple Play, a combination of services that adds a lot more convenience to home telecom services.
Embratel1 (Public, NYSE:EMT), in partnership with NET2 (Public, NASDAQ:NETC), is launching in Brazil an international trend: Triple Play, a combination of services that adds a lot more convenience to home telecom services. It is about 3 services over one single cable access: Broadband Internet + TV + Wireline PHone. The Scientific-Atlanta3 AllStar DPX2203 equipment is leased by Embratel on a loan for use basis and is delivered, installed and tested by NET.
No special phone set is required. Any set (DTMF standard- tone dial-up) can be used, including cordless phones. The calls are placed from this phone set, and the user do not need to use computer or access the Internet to call.
With NET fone Via Embratel the user can place local, long distance domestic (DDD) and international (IDD) calls to wireline and cell phones. The value of the monthly exemption can be used with any type of local , long distance domestic (DDD) and international (IDD) calling over the 21*, to wireline and cell phones. If the monthly consumption exceeds the exemption, rates for the exceeding calls are charged to the bill.
[1] Embratel Participacoes S.A. (Embratel Holdings) is a telecommunications services provider, operating domestic and international long-distance, data communications and local services. The Company is a provider of data and Internet services in Brazil. Its data transmission network, which incorporates fiber optic, digital microwave, satellite and copper transmission technology, allows the Company to provide a range of broadband data services to a client base.
[2] Net Servicos de Comunicacao S.A (Net Servicos) is a pay-television operator in Latin America. As of December 31, 2005, the Company had approximately 1.5 million connected subscribers in 44 cities in Brazil, including Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro. It is also a provider of high-speed cable modem Internet access through its NET Virtua service, which had approximately 367,000 subscribers as of December 31, 2005.
[3] Scientific-Atlanta is one of the largest makers of set-top boxes used by cable subscribers to receive TV programming and interactive online services such as movies-on-demand, e-mail, and Web connection. Although set-top boxes account for a large portion of sales, the company also makes digital video recorders (DVRs), cable modems, and network transmission and distribution equipment (digital video compression products, multiplexers, and signal encoders/decoders) used in the central offices of broadcasters. In early 2006 Scientific-Atlanta was acquired by Cisco Systems for about $6.9 billion.
Internet Television Broadcasting
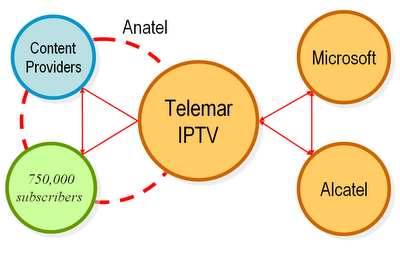 Telemar 1 a private Brazilian telecom operator serving three-quarters of a million subscribers, plans to announce its preferred platform for offering IPTV - Internet Protocol TV (Internet TV) services before the end of August. The operator plans to test IPTV with up to a thousand users this year ahead of a full-blown launch in 2007. It has short-listed three manufacturers to provide it with equipment and although it has not named names, the leading contenders are though to be a joint initiative by French equipment supplier Alcatel and US software giant Microsoft.
Telemar 1 a private Brazilian telecom operator serving three-quarters of a million subscribers, plans to announce its preferred platform for offering IPTV - Internet Protocol TV (Internet TV) services before the end of August. The operator plans to test IPTV with up to a thousand users this year ahead of a full-blown launch in 2007. It has short-listed three manufacturers to provide it with equipment and although it has not named names, the leading contenders are though to be a joint initiative by French equipment supplier Alcatel and US software giant Microsoft.Telefonica de Brasil (Telesp), which passed one million DSL subscribers in 2005, was the first Telefonica subsidiary to launch an RFP (Request for Proposals) for IPTV and a small trial is progressing slowly. And Brasil Telecom, with its 900,000 ADSL lines, has already shown a taste for the video business with its VOD-over-public-Internet service, offering sports, music and lifestyle programming. A number of telcos are working to get the Brazilian government to deregulate video and IPTV market.
Facing increasing competition from mobile phones and the resurgent cable industry, Brazilian fixed operators are getting ready to deploy IPTV. While the challenges for Brazilian IPTV will be numerous, not all is lost of for fixed operators. The primary value proposition of IPTV is as a broadband solution bundled in triple- or quadruple-play packages. The relatively low pay-TV penetration in Brazil therefore represents an opportunity for the country’s operators, who may be able to use IPTV as a catalyst for pay-TV expansion.
IPTV is becoming part of our culture a long time ago before the brazilian government have chosen the japanese DTV digital television system wich is expected to bring the digital television to 92 million recievers spread abroad Brazil´s 8,500,000 sq km.
Brazilian Internet Television has been tested in various ways in the last 4 years (as well by mobile phones operators). There are too many good examples of television services over DSL in Brazil and now it is time to acheive commercial success among broadband subscribers. Websites like Globomediacenter by Globo.com and Bandnews are broadcasting their signal through Internet at DSL speed to the world.
[1] Telemar Norte Leste S.A. (Public, SAO:TMAR5) is engaged in telecommunication services in Brazil. The Company is a specialty provider of local and long-distance landline telephone networks for residential, small business and corporate clients. In addition, it offers international fixed telephony, public telephones, Internet services, videoconferences, image messages and data communications.
Bank of Brasil Pocket Bank
These expenses were US$ 1.22 billion (R$ 2.58 billion), or 16.7%, greater than those made in the previous year. In 2004, financial institutions in Brazil invested US$ 7.3 billion (R$ 15.4 billion) in technology, 10.5% of net assets. According to the Brazilian Federation of Bank Associations (Febraban), the tendency is for further growth this year.
"Brazilian banks, pioneers in ample use of electronic trade in Brazil, have already identified that the future is in doing business in the digital era," according to the FGV-SP study. Internet Banking and Mobile Banking are some of the areas in which financial institutions are investing.
The FGV's Annual Cost per Keyboard (CAPT) at banks is US$ 22,000 dollars, whereas in the service sector the total is US$ 10,000, in industry, US$ 9,000, and in trade, US$ 6,400. This index is determined by total investment divided by the number of keyboards installed in companies, including terminals at Automatic Teller Machines and cashiers.
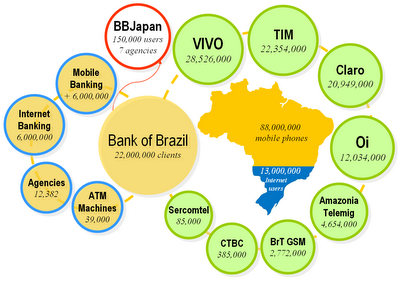 Bank of Brazil1 is revolutionizing the CAPT index launching the 3ª wave of banking attendance in the country. The first wave was to take the customers of the attendance box to be taken care of in ATMs terminals; the second wave was to place the "Internet bank" to the reach of the customers at their homes or offices; now the third wave is to place the "mobile bank" literally in the hands of its customers.
Bank of Brazil1 is revolutionizing the CAPT index launching the 3ª wave of banking attendance in the country. The first wave was to take the customers of the attendance box to be taken care of in ATMs terminals; the second wave was to place the "Internet bank" to the reach of the customers at their homes or offices; now the third wave is to place the "mobile bank" literally in the hands of its customers.Today, Brazil has an active market of about 88 million cellular devices, in counterpart counts "only" on 13 million people with access to the Internet. What it demonstrates the existence of a very great number of people with capacity to participate of this type technological solution.
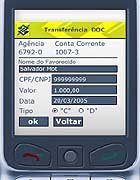 Today the BB mobile bank user can make since mere extract and balance consultations until sophisticated transactions as accounts payments, transferences between banks, BB has launched the possibility of the customer to catch an electronic loan and also has an innovation of the Bank of Brazil that is you to catch a consigned loan direct from the mobile device. One another interesting operation is the the prepaid customer is being able to recharge his mobile from the bank account. Today, 26% of almost the 3 million transactions that people carry through in "mobile bank" are related to the user mobile itself. This is a good indication, that the users who are using the solution also are using of daily prepaid and many times do not have access to the Internet.
Today the BB mobile bank user can make since mere extract and balance consultations until sophisticated transactions as accounts payments, transferences between banks, BB has launched the possibility of the customer to catch an electronic loan and also has an innovation of the Bank of Brazil that is you to catch a consigned loan direct from the mobile device. One another interesting operation is the the prepaid customer is being able to recharge his mobile from the bank account. Today, 26% of almost the 3 million transactions that people carry through in "mobile bank" are related to the user mobile itself. This is a good indication, that the users who are using the solution also are using of daily prepaid and many times do not have access to the Internet.The developer EverSystems is known by the financial area supplying solutions. Responsible for the creation of a mobile banking solution for the Vivo-BB operation, based on the BREW technology , the company now created the new BB version of mobile banking, based on J2ME technology.
The Bank of Brazil has also initiated its operation of pocket bank this week in Japan. The BB will be the first Brazilian financial institution with performance in that country to offer this service to the nipo-Brazilians. The bank has seven agencies in that country, besides keeping partnership with the post offices local for attendance to about 105 a thousand customers in the country. The new service will allow that the customers of the BB also have access its accounts in Japan and in Brazil.
[1] Bank of Brazil (Public, SAO:BBAS3) is the greater retail bank of the Country and possesss currently about 22 million customers. The BB has invested in the magnifying of the forms of attendance by means of electronic channels. With a platform of 39 a thousand terminals spread for the Country, the BB has today a base of 22 million account holders, who carry through 88% of its banking transactions from the auto-attendance service. Internet answers for 36% of the total of these atendances.
Prepaid business model
 Prepaid refers to services paid for in advance. Some examples include gift cards, preloaded credit cards, tolls, and cell phone usage credit, among other items.
Prepaid refers to services paid for in advance. Some examples include gift cards, preloaded credit cards, tolls, and cell phone usage credit, among other items.Prepaid phone cards began in the late 1970's in Italy. The purpose was to provide convenient phone calling for travelers and to combat payphone vandalism1. It wasn't until 1992 that the debit phone card began in the US.
Prepaid services and goods are sometimes targeted to marginal customers by retailers. Prepaid options can have substantial cost reductions over postpaid counterparts because they allow customers to monitor and budget usage in advance.
 Recent statistics (OECD Communications Outlook 2005) indicate that 40 % of the total mobile phone market in the OECD region consists of prepaid accounts. In some countries, such as Italy, Spain or Mexico, market share of prepaid can be as high as 90 %. In other countries, such as Finland or South Korea, the figure drops to about 2 %.
Recent statistics (OECD Communications Outlook 2005) indicate that 40 % of the total mobile phone market in the OECD region consists of prepaid accounts. In some countries, such as Italy, Spain or Mexico, market share of prepaid can be as high as 90 %. In other countries, such as Finland or South Korea, the figure drops to about 2 %.It seems that after serving well to the mobile phone market on countries like Brazil, Russia, India and China the prepaid card business model is opening the doors to other services.
The first nonphone-card prepaid programs were launched in the mid-1990s by national retailers such as Blockbuster Video and Kmart2. And now with services such as Flexgo (Microsoft), Wi-fi Internet (Velox), Brazilian AICE fixed phone (Anatel) gives their users the opportunity to access a lot of communications services that even in the 21st Century would last another century to be in the hands of low income population if not for those innovative business models.
Another service thought to follow prepaid model is the Ampla one, deliverer of energy services in 66 cities of Rio de Janeiro, who intends to launch this year the prepaid light account. Through a 0800 telephone number, the user goes to determine how much he wants to pay of energy by month. And, by his mobile phone, the user will be advised when his credits would be depleting.
[1] In fact there was a shortage of coins in Italy at the time and payphone theft was common. Cards were introduced with a magnetic strip on the back for use in special phones to combat the coin shortage.
[2] Tom Locke, “Billions in Gift Cards: First Data Plans to Add Loyalty Feature in ’05,” Denver Business Journal, December 10, 2004 print edition.
BNDES Innovation Fund
The Technology Fund launched last week (21 June) will sponsor projects that relate to economic and social development in specific subject areas, including agricultural biotechnology, drugs for neglected diseases, software and semiconductors.
Research into generating energy from biomass — such as developing fuel based on alcohol derived from fermented sugar cane — will also be eligible.
The bank has already invested US$128 million in such projects. The existing projects will be competing with new ones for the technology fund's grants.
The fund is intended to support projects that find technological solutions to problems already identified by Brazilian research institutes and economists.
It also aims to promote innovation by backing ideas that look set to introduce new products onto international markets, something that Brazil has not excelled at to date.
"Technology and innovation are critical factors for the country's development", says Aluísio Asti, one of bank's economists who helped set up the fund. Asti said the Technology Fund would operate in line with the bank's innovation policy that was introduced in 2005.
GOL Airlines
 GOL Linhas Aereas Inteligentes SA (Public, NYSE:GOL) is a low-fare, low-cost airline based in São Paulo, Brazil.
GOL Linhas Aereas Inteligentes SA (Public, NYSE:GOL) is a low-fare, low-cost airline based in São Paulo, Brazil. The airline was established in 2000 and started operations on 15 January 2001. It is a subsidiary of Brazilian conglomerate Grupo Aurea, which has other transport interests including Brazil's largest long-distance bus company. Grupo Aurea in turn is owned by the Constantino family. Gol's unprecedented low fares revolutionized the domestic Brazilian air travel market. As of 2004, Gol had carried 11,600,000 passengers, and constituted 20% of the Brazilian air travel market. On 24 June 2004 Gol launched simultaneous initial public offerings on the New York and Sao Paulo stock exchanges. It is now owned by AeroPar Participacoes (77%), Venture (17.6%) and American International Group (5.4%) and employs 3,303 staff. The growth in Gol`s stock price made the Constantino family a member of the Forbes` billionaire list in 2005.

As the first discount airline in South America, Gol has modeled itself after the American discount flight giant Southwest and has rapidly made large profits.
Gol chief executive officer Constantino de Oliveira Junior, said: "We've made flying popular, we've extended the Gol effect to Brazil and South America by expanding our business, with innovation, efficiency, quality service and disciplined control of costs and rates."
"What made the difference was that Gol arrived on the scene with a new fleet. As a result, its maintenance costs were extremely low. In addition, it was operating on routes that were short and had a high density of traffic. It was selling tickets almost exclusively on the Internet, the way it is still doing today.” According to Oliveira, that approach means that Gol enjoys considerably lower sales costs per ticket.
Gol has managed to change some paradigms of the Brazilian aviation sector, which traditionally valued such concepts as sophistication, elegance and glamour when marketing air travel. The big concepts were broken by the simplicity, practicality and simplification of Gol’s operations.
Currently Gol has 41 flights between Brazil and neighboring Argentina. Most of its major destinations can be reached on direct flights from Miami, Dallas and Los Angeles.
* GOL Linhas Aereas Inteligentes SA Brazil's leading discount airline. The Company provides frequent service on routes between all of Brazil's major cities and to international destinations in Argentina, Bolivia, Paraguay and Uruguay. As of December 31, 2005, it operated 42 single-class Boeing 737 aircraft, and offered 420 daily flights in Brazil and to its international destinations.
Habib's Food Franchise
 THE BIGGEST BRAZILIAN FAST FOOD CHAIN, HABIB'S* opened its first shop in 1988, in Sao Bernardo do Campo, Sao Paulo state. Since that has innovated in various ways delivering new products and services that combine efficiency, originality but above all a clearly respect and knowledge about its market, the low and middle income population.
THE BIGGEST BRAZILIAN FAST FOOD CHAIN, HABIB'S* opened its first shop in 1988, in Sao Bernardo do Campo, Sao Paulo state. Since that has innovated in various ways delivering new products and services that combine efficiency, originality but above all a clearly respect and knowledge about its market, the low and middle income population.Low prices, variety and high performance in quality are the foundations which have brought Habib´s two prizes by ABF - Brazilian Franchising Association and an Alshop - Brazilian Association of Shopping Vendors prize (the brazilian retailer "oscar").
The Habib's relationship politics with its customers and the adjustment to the Brazilian pockets, brought in these 16 years a recognized success together the average consumer. The company presents respectable numbers as 120 million meals served/year, beyond a patrimony of 12 a thousand employee right-handers, responsible for all the operacionaliztion of the brand an essential part of the Habib's success.
The growth index translates the investments carried through in the 9 central offices of manipulation and distribution of menu itens, delivered through more than 260 shops in the main regions of the country.
 Habib´s has also innovated on the structural and intelectual capital of the company in building 9 interdependent enterprises that work toghether on the operationalization of the brand: an Industrial Bakery (Arabian Bread), 2 Ice cream factories (Ice Lip's and Portofino), Dairy products (Promilat), Contact Center (VOXLINE), Marketing (PPM), Engineering and Projects (Vector 7), Franchising (Franconsult) and Real estate Consulting (Planej).
Habib´s has also innovated on the structural and intelectual capital of the company in building 9 interdependent enterprises that work toghether on the operationalization of the brand: an Industrial Bakery (Arabian Bread), 2 Ice cream factories (Ice Lip's and Portofino), Dairy products (Promilat), Contact Center (VOXLINE), Marketing (PPM), Engineering and Projects (Vector 7), Franchising (Franconsult) and Real estate Consulting (Planej). The most popular products at Habib's are the esfiha - a small, round flatbread topped with minced beef or cheese - and the kibe - a croquette of beef shaped like a rugby ball.
The most popular products at Habib's are the esfiha - a small, round flatbread topped with minced beef or cheese - and the kibe - a croquette of beef shaped like a rugby ball.These are deliberately priced as low as possible. Esfihas sell for 69 Brazilian centavos (31 cents) each, with the price falling to 39 centavos in some special offers.
Although people of Arab descent make up a mere 7% of the Brazilian population, delicacies as hummus, stuffed vine leaves and tabouleh as part of its menu are being delivered at this time in less than "28 minutes" at home in every city that has a Habib's store.
Habib's
Sao Paulo, Brazil
Telephone: + 55 0800 775 6000
Site: www.habibs.com
* Habib's is a Brazilian fast food chain. Specialising in Arabic cuisine, it has more than 260 outlets across the country and has recently begun expansion into foreign markets. Habib's is the second largest fast food chain in Brazil, second only to McDonald's.





